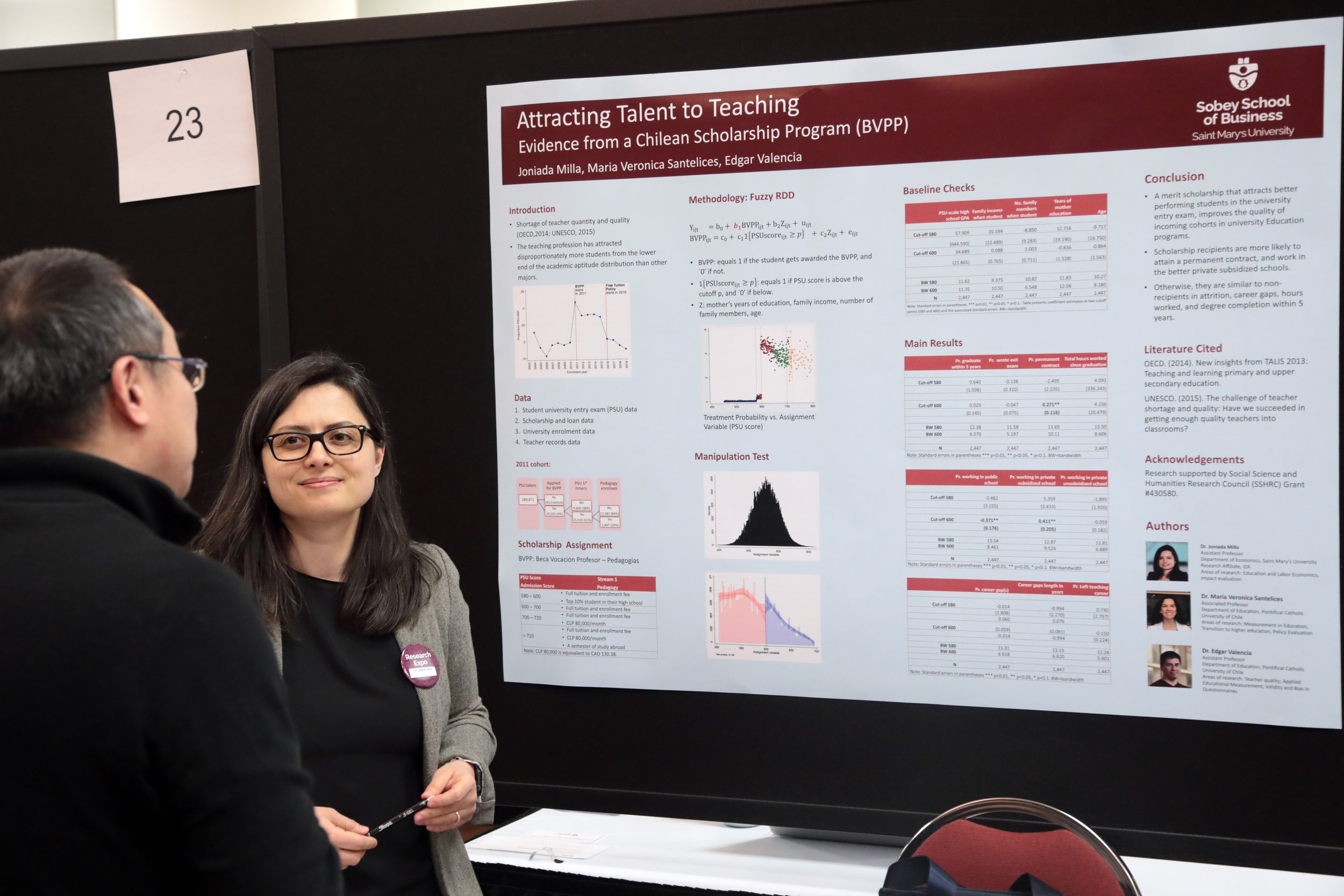
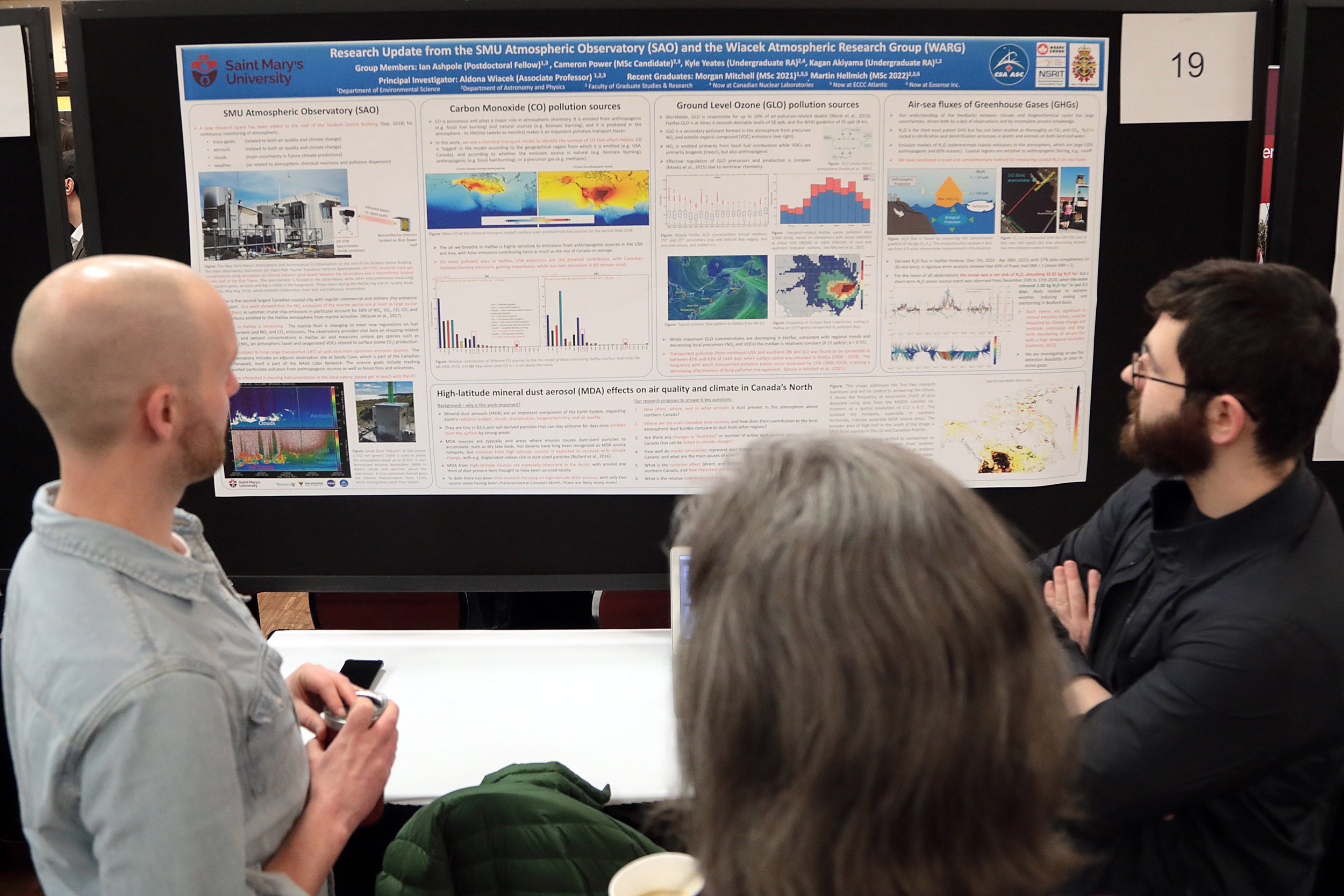
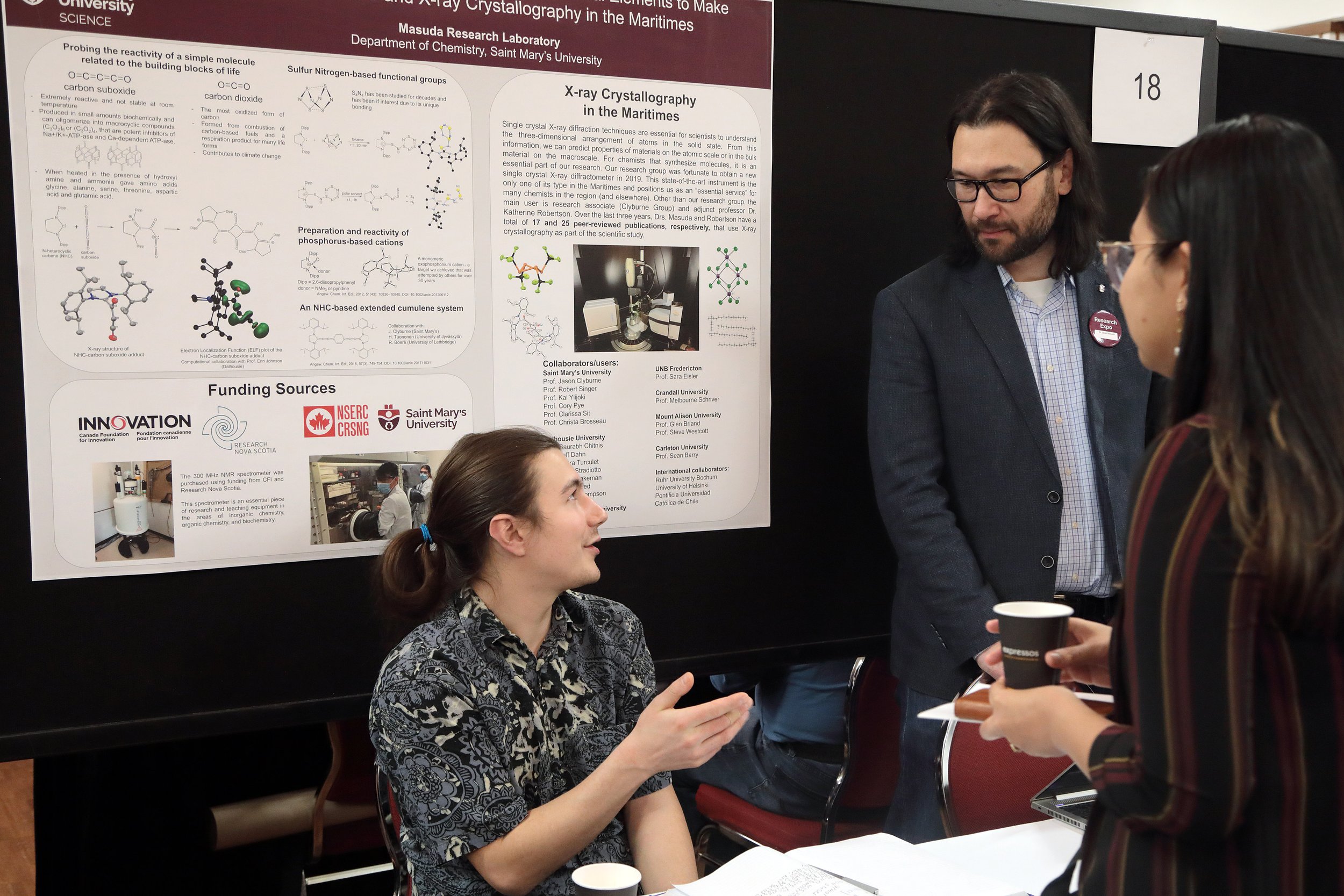
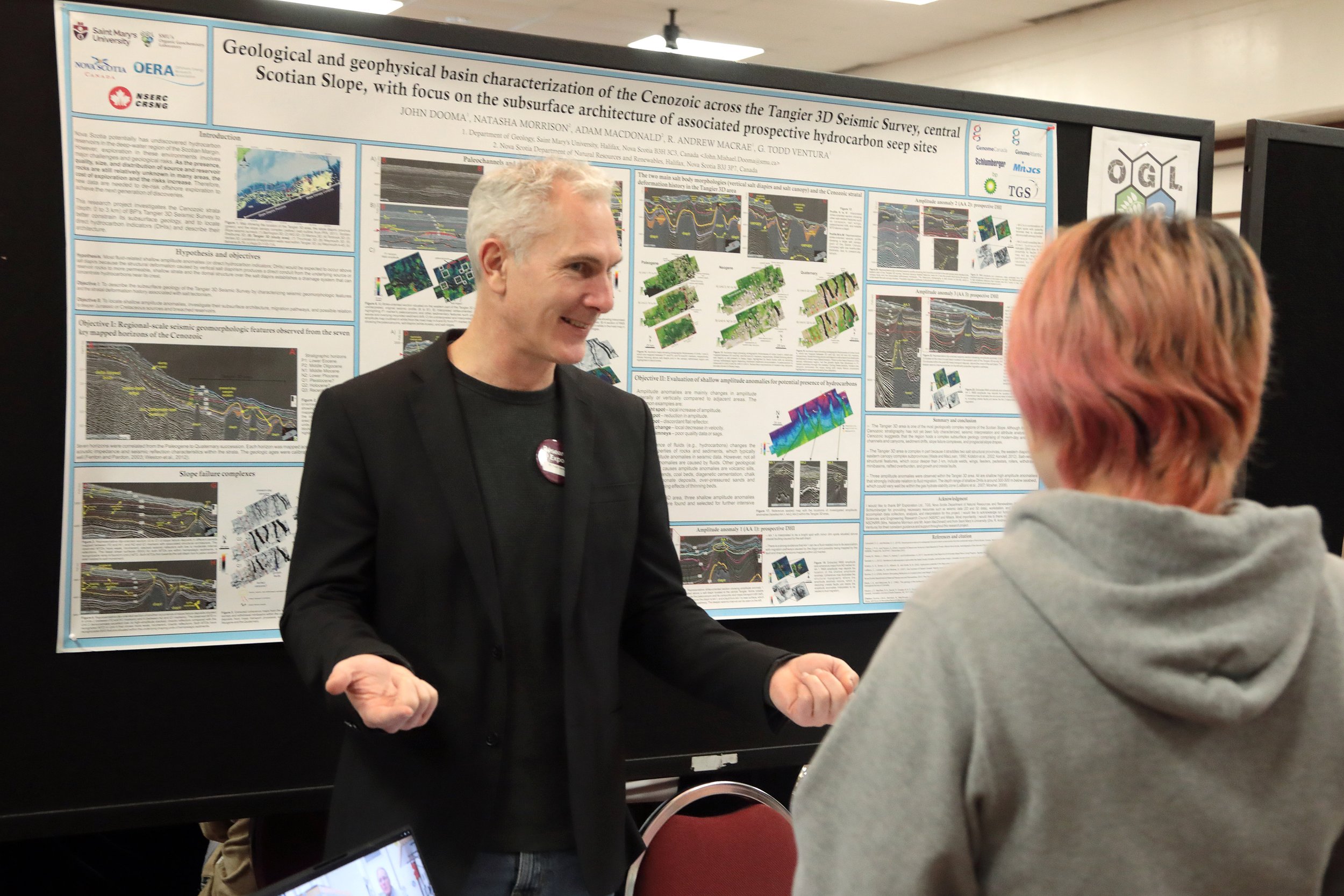
Dr. Mary Sheppard wins the Father William A. Stewart Medal for Excellence in Teaching. Her PhD research focused on how students learn chemistry.
L-R: Alumni Association member Fiona King BComm’93, SMU President Dr. Robert Summerby-Murray, and Dr. Mary Sheppard at Spring Convocation.
First-year chemistry classes introduce students to an exciting field of science—with new terminology and research methods, and the opportunity to study in a university laboratory setting for the first time.
Arriving at Saint Mary’s from Halifax or homes around the world, students’ first university classes can be an exciting, eye-opening experience—and a big adjustment.
Luckily, these new students at Saint Mary’s have an award-winning professor who understands the challenges they face. As a first-generation university graduate from Taylor’s Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, Dr. Mary Sheppard still remembers leaving her small community for Memorial University.
“Leaving my family behind and going to the ‘big city’ of St. John’s was huge for me, and I understand what our rural students, and those from close-knit communities, are missing,” said Dr. Sheppard.
Finding the right path in her academic career meant being flexible and open to new paths.
“At first I wanted to be a pharmacist,” explained Dr. Sheppard. “When I was growing up in rural Newfoundland there was no access to career counseling. If you got good grades you were told you should be a pharmacist, nurse or doctor…I didn’t want to be a nurse or doctor—too much blood.”
It was her first-year chemistry professor who suggested that pharmacy might not be the best fit for her, and offered a chance to do a summer project that led to more than two decades studying and teaching chemistry.
“Growing up, I didn’t even know that a career in chemistry was a possibility,” said Dr. Sheppard. “I tell my students to keep an open mind. You don’t have to stick with what you first thought you wanted to be—I wouldn’t have been happy as a pharmacist.”
Along with teaching first-year classes as a senior lecturer, for the past five years, Dr. Sheppard was also a student, pursuing a PhD at the University of New Hampshire.
Dr. Mary Sheppard
Dr. Sheppard’s PhD research has made her uniquely qualified for her role teaching at the university level. Her interest in how students learn led her to pursue the topic of chemistry education research for her doctoral degree. She explains that during the first few weeks of classes, she intentionally slows the pace to let students adjust to the environment.
“For some students, the lab can be very daunting because they didn't have a lab in high school—coming from a big city high school is not the same as any rural area in the world,” she says. “As part of our student success program, their first experience in that room isn’t an experiment—they go into the space as part of a scavenger hunt around campus…it helps them get oriented first.”
Once the term is underway, students will look forward to performing guided inquiry experiments along with a more traditional curriculum of procedural experiments. Guided inquiry prepares students for real-world work by challenging them to design an experiment to tackle a problem, tweaking it in the lab and submitting their group’s finalized experiment.
“Learning how to approach a problem teaches creative thinking— if the procedures don’t all work out perfectly, they learn more from that,” she says.
In her PhD research, Dr. Sheppard looked at how students learn about pH buffers, a chemistry topic that many find difficult to grasp. “I was trying to figure out why is this so tough for students—what are the roadblocks,” she explained. First, she interviewed students at the University of New Hampshire using a “think out loud” approach, recording them as they worked through problems. A qualitative analysis followed, allowing her to design teaching strategies that matched students’ successes and challenges.
“It was interesting to see that while the American students might have different backgrounds, they have the same or similar challenges that our students have.”
Her last goal for her PhD was to design a teaching strategy that addresses those challenges, setting students up for success. After many years of teaching, the instinct to help students is strong.
“You have to separate yourself from the student, you can’t help them because you want to see what they’re thinking and what the issues are,” she explained. “I think I ground the enamel off my teeth because I kept wanting to jump in and help.”
This research is beneficial to students in the classroom and lab and may lead to changes in how the topic is introduced in textbooks.
“Textbooks come from an expert point of view, but if you’re not an expert yet, that approach can be frustrating,” she explained. “One of the tenets of teaching pedagogy is that it’s not about knowing the topic, it’s about knowing how to teach it.”
Dr. Sheppard explained that like most PhD topics, hers was very narrow in focus. But she says it also exposed her to literature and people at conferences who are talking about different ways to teach.
“Understanding better how students learn at a higher level, it’s easier to transfer that knowledge to other areas of chemistry,” explained Dr. Sheppard.
Dr. Sheppard’s history of successful teaching and her drive to continuously build on that success have been recognized. This spring she won the Father William A. Stewart. S.J. Medal for Excellence in Teaching, the top teaching award at Saint Mary’s. The award is determined by nominations from alumni, students and colleagues and is awarded to a professor who has made significant contributions to the education of Saint Mary's students through excellence in teaching and service.
Father Stewart was known for his strong beliefs in promoting accessible education to marginalized communities and was also very much involved in promoting teaching innovation and excellence on campus. The award honours this legacy.
After receiving the award at the May convocation ceremony, Dr. Sheppard travelled to the U.S. where she received her PhD at the University of New Hampshire.
Congratulations Dr. Sheppard!