Sometimes climate leadership looks like a homeowner choosing a thriving habitat over a quick-fix retaining wall.
TransCoastal Adaptations (TCA), the Saint Mary’s University-based Centre for Nature-Based Solutions, has announced a major milestone for coastal resilience: the first certified Green Shores for Homes projects in Atlantic Canada.
Two waterfront properties, located at Kingsburg Beach and Molega Lake in southwest Nova Scotia (Kespukwitk), have both achieved Gold-level certification, the highest standard under the program.
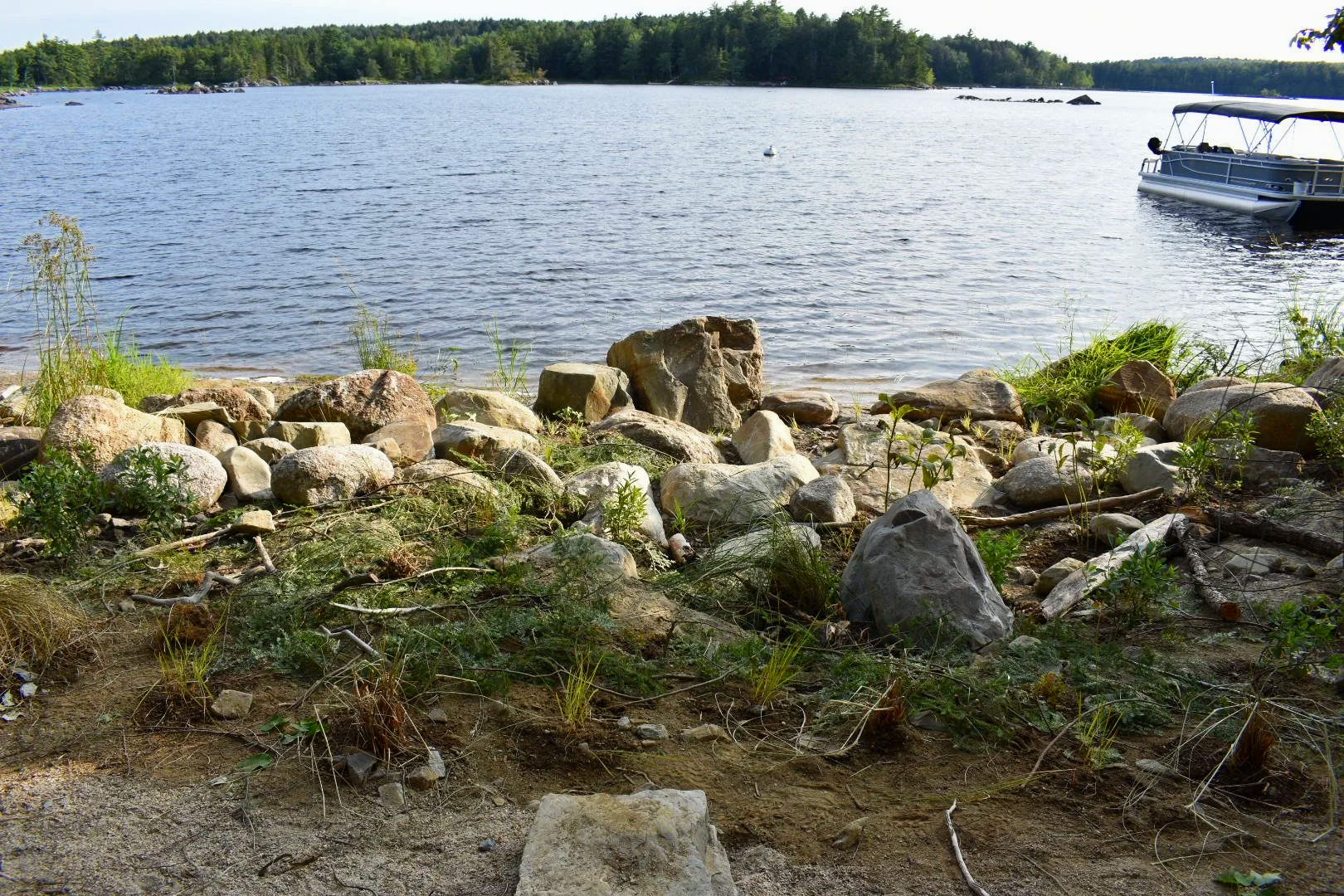
For decades, waterfront improvements have often involved installing rock walls or concrete that can unintentionally worsen erosion and destroy local ecosystems. The Green Shores for Homes program, coordinated in the Maritimes by the TCA team at Saint Mary’s, offers a different path.
Dr. Danika Van Proosdij, Saint Mary’s University Professor and Director of TransCoastal Adaptations
“These projects prove that climate adaptation and biodiversity protection can go hand-in-hand,” says Dr. Danika Van Proosdij, Coastal geomorphologist and professor in the Department of Geography and Environmental Studies at Saint Mary’s University, as well as the Director and Co-Founder of TCA.
“By working with natural processes rather than against them, these homeowners are protecting their properties while also strengthening the health of our coastlines,” she says.
Southwest Nova Scotia is a recognized biodiversity hotspot, home to many species at risk. These Gold-certified sites serve as practical models for how individual actions can contribute to broader environmental outcomes:
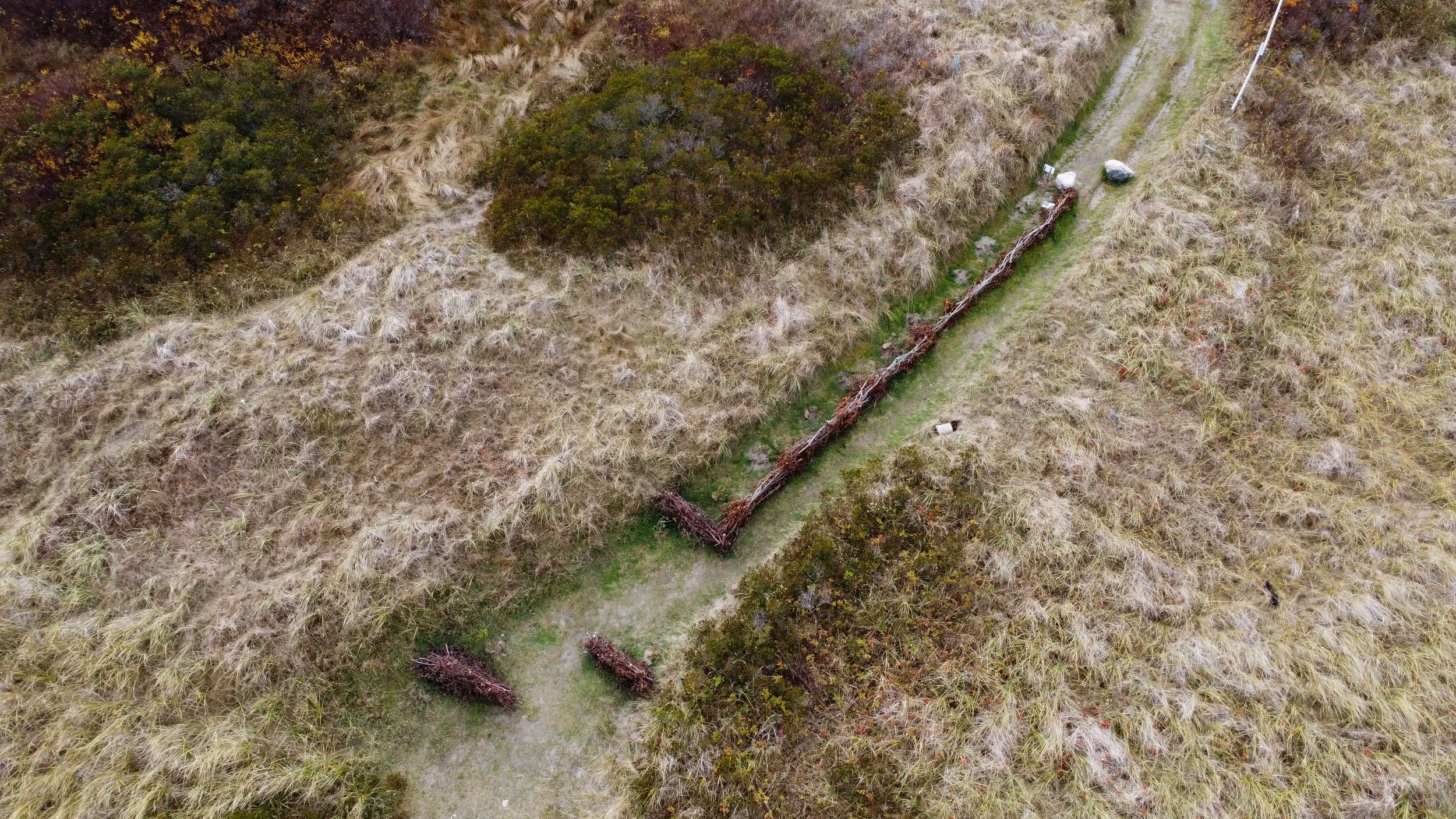
At Kingsburg Beach, erosion mitigation and sand-capture techniques were implemented to stabilize the shoreline while maintaining natural coastal dynamics.
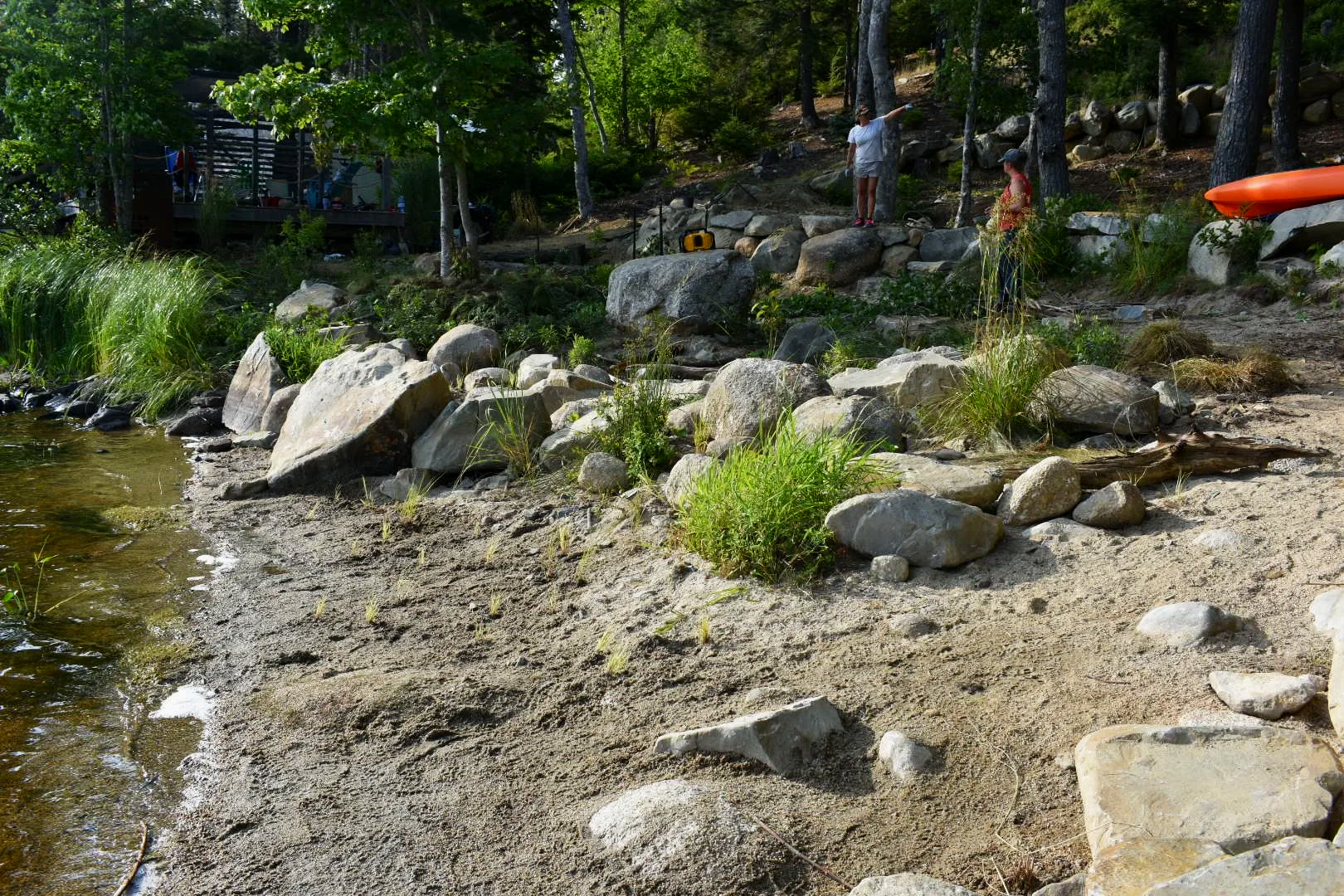
At Molega Lake, a full riparian zone restoration was completed, creating a natural buffer that improves water quality and increases resilience to flooding.
“The impact of these projects extends past the property lines,” says Dr. Van Proosdij. “The homeowners on these two properties treated their certification as a starting point for advocacy, engaging with their neighbours and local communities on shoreline health.”
True to the Saint Mary’s mission of community-engaged research, these projects bring together a wide range of expertise. While TCA provided the framework, the work on the ground was supported by:
Helping Nature Heal Inc. and CB Wetlands and Environmental Specialists (Design and implementation)
Manzer Brothers Excavation and Landworks Inc. (On-the-ground support)
The Mersey Tobeatic Research Institute and Government of Nova Scotia biologists (Specialized knowledge of Atlantic Coastal Plain flora and endangered reptiles)
As climate pressures like rising sea levels and storm intensity continue to affect Atlantic Canada, the success of the Kingsburg and Molega Lake projects is a proven example that coastal living can be protected by working in partnership with nature, one shoreline at a time.
To learn more about Green Shores for Homes and how TransCoastal Adaptations is leading nature-based climate solutions, visit transcoastaladaptations.com.
Event on campus
Join Dr. Van Proosdij for an upcoming event with Dr. Jonathan Fowler: "Re-imagining resilience in Bay of Fundy Dykelands."
Thursday, February 26, 2026
6-8:30 p.m.
Unilever Lounge, 4th floor Sobey School of Business
923 Robie St.
Welcome to the first annual fireside chat in the series Reimagining Rural Resilience: Changing Landscapes and Lifescapes. Hosted by The Gorsebrook Research Institute for Atlantic Canada Studies (GRI), the TransCoastal Adaptations Centre for Nature-Based Solutions (TCA) at Saint Mary's University, and the Community Conservation Research Network (CCRN), this series will showcase new research on and about Nova Scotia with the public.
This is a friendly fireside chat, open to everyone. Light refreshments provided. Together, let's learn about the latest research beyond barriers of university classrooms. Register here.